Laparoscopic Surgery
What is Laparoscopic surgery?
Laparoscopic surgery, also called minimally invasive surgery
(MIS), bandaid surgery, keyhole surgery is a modern surgical technique
in which operations in the abdomen are performed through small incisions
(usually 0.5–1.5 cm) as compared to larger incisions needed in
traditional surgical procedures.
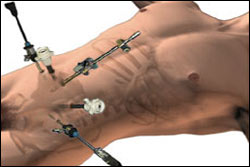
Keyhole surgery uses images displayed on TV monitors for magnification
of the surgical elements.
Advanced Laparoscopic surgery includes operations within the abdominal
or pelvic cavities, whereas keyhole surgery performed on the thoracic or
chest cavity is called thoracoscopic surgery. Laparoscopic and
thoracoscopic surgery belong to the broader field of endoscopy.
There are a number of advantages to the patient with laparoscopic
surgery versus an open procedure. These include reduced pain due to
smaller incisions and hemorrhaging, and shorter recovery time.
Today there is no abdominal surgery which is not performed
laparoscopically.
The Digital laparoscope
In the digital laparoscope the charge-coupled device is placed at the
end of the laparoscope, eliminating the rod lens system.[1] Also
attached is a fiber optic cable system connected to a 'cold' light
source (halogen or xenon), to illuminate the operative field, inserted
through a 5 mm or 10 mm cannula or trocar to view the
operative field. The abdomen is usually insufflated, or essentially
blown up like a balloon, with carbon dioxide gas. This elevates the
abdominal wall above the internal organs like a dome to create a working
and viewing space. CO2 is used because it is common to the human body
and can be absorbed by tissue and removed by the respiratory system. It
is also non-flammable, which is important because electrosurgical
devices are commonly used in laparoscopic procedures.
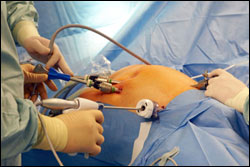
Advantages
There are a number of advantages to the patient with laparoscopic
surgery versus an open procedure. These include:
- Reduced bleeding, which reduces the chance of needing a blood
transfusion.
- Smaller incision, which reduces pain and shortens recovery
time, as well as resulting in less post-operative scarring.
- Less pain, leading to less pain medication needed.
- Although procedure times are usually slightly longer,
hospital stay is less, and often with a same day discharge which
leads to a faster return to everyday living.
- Reduced exposure of internal organs to possible external
contaminants thereby reduced risk of acquiring infections.
|
Dr Manubhai Pipalia has extensive experience in :
|
|